Continuous motion assembly machine: What are the best tips for mounting electronic devices?
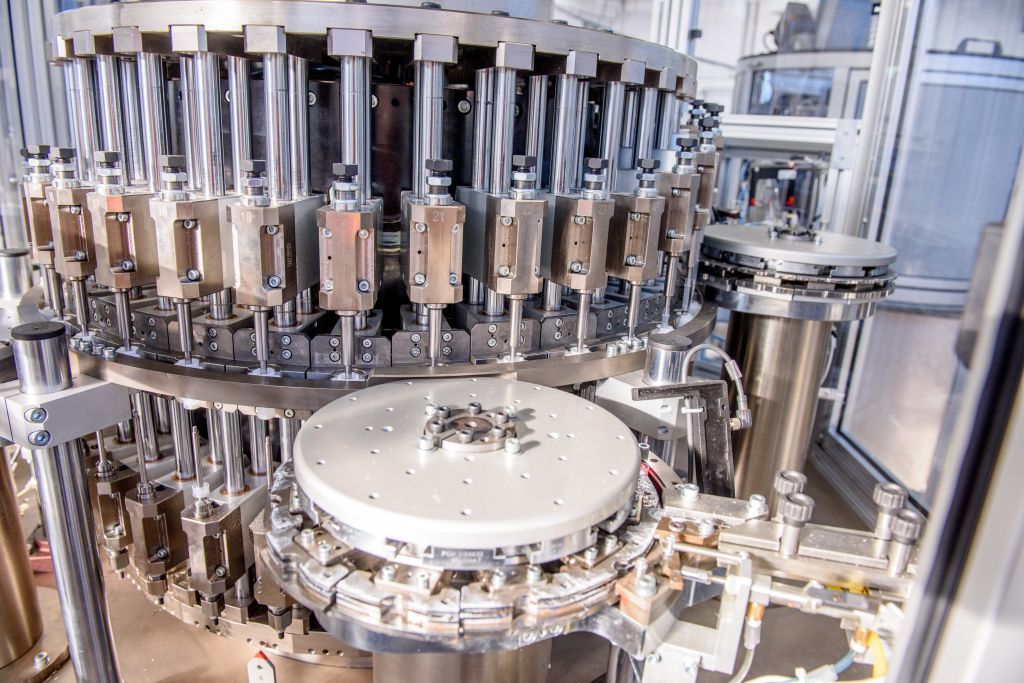
Successful assembly of electronic products within a manufacturing environment requires strategic organization of manufacturing areas, maintenance of automated continuous motion assembly machine, motivation of workers, and thorough testing of devices.
In addition, the assembly area must have regulations regarding static control to avoid accidental power surges that damage sensitive electronic components. Spacing between all assembly areas should also be considered so that efficiency remains high.
Electronics assembly must be performed in a certain series of steps, from the initial board bonding processes to the joining of the final components.
As a result, each manufacturing area must be arranged in the order of the steps; materials cannot be zigzagged through a production hall, as efficiency will be significantly reduced. For example, manufacturing area «A» should be close to area «B» and «C».
Automated machines perform most modern electronics assembly processes. Any unexpected breakdown can be costly to the manufacturer; managers should have preventive maintenance programs for each machine.
Continuous motion assembly machine must be properly adjusted and lubricated on a regular basis to minimize breakdowns. Workers must also be well versed in troubleshooting small machines during the manufacturing process; experienced workers can repair a small problem before it becomes a major problem that affects manufacturing time.
The human element is also important in the assembly of electronic components. Workers must have a management team that emphasizes teamwork and motivation; each worker must feel valued and comfortable in his or her position.
For example, workers who are comfortable with their skills should be able to quickly access concerns about a malfunctioning machine or defective product and notify their immediate supervisor. Working as a team will help keep the product viable and the company efficient.
Quality assurance is a key factor in the assembly of electronic components. Each part of the device should be tested individually to determine overall functionality before moving on to the next area of the assembly process.
The final product should be tested in the same way a customer would use the item; if possible, workers should take it into the field to verify that the internal electronics can withstand the weather elements.
Static control is a major concern during electronics assembly. The production floor should have static control mats; workers should also have grounding straps strapped to their ankle or wrist during electronic handling.
Any static discharge can damage individual components or the entire board, resulting in costly waste. The floor of the continuous motion assembly machine line should have enough space between work areas for adequate movement of workers, but not too much space so that employees must walk long distances.
Transporting electronic components over long distances can generate static loads throughout the work area; walking long distances also reduces overall production efficiency.